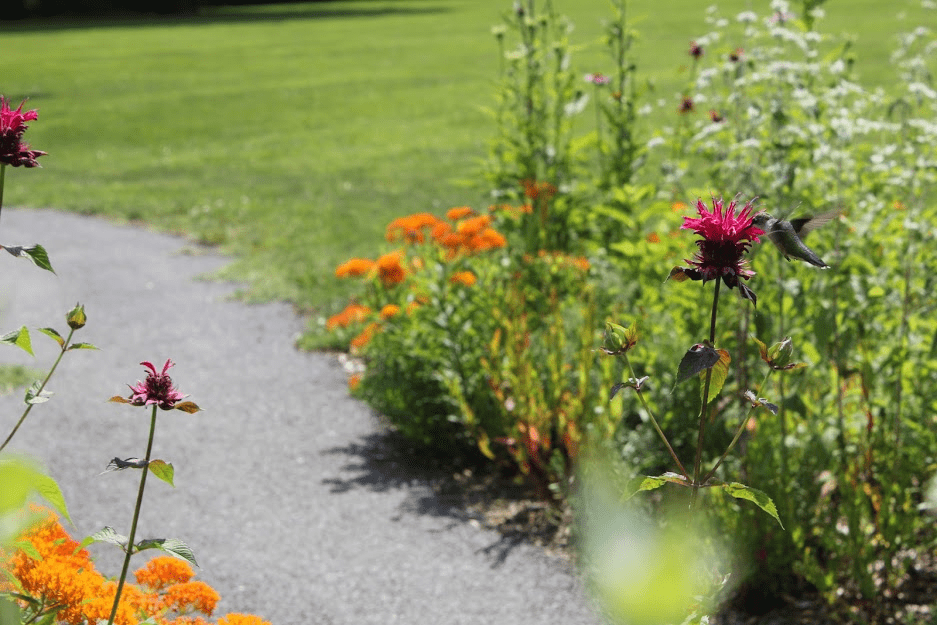We have much more to do and your continued support is needed now more than ever.
Four Questions about Neonicotinoid Pesticides
The increasing buzz on pollinators has raised awareness on the various threats to their survival, such as habitat loss and chemical use. For over 42 years, the National Wildlife Federation’s Garden for Wildlife program has been ahead of these issues by educating and empowering people to restore habitat for bees, butterflies and other pollinators in their own yards and by gardening in natural, sustainable ways.

With the increased media awareness on pollinators and the potential dangers of neonicotinoids to them, many concerned gardeners and wildlife-lovers are seeking more information on what exactly these chemicals do and how to avoid them. Here are answers to four of the most commonly asked questions:
What are neonicotinoids?

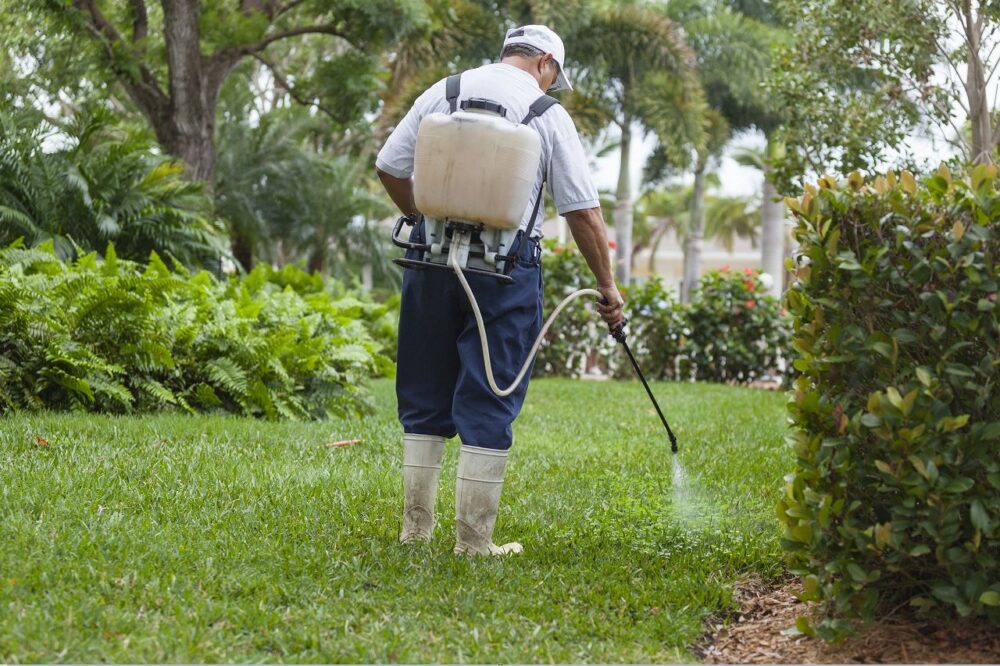
Neonicotinoids are systemic chemicals, meaning that they are absorbed by the plant, protecting it from chewing and sap-sucking insects. They are absorbed by all parts of the plant, including the sap and pollen. Therefore, once neonicotinoids are applied, they cannot be washed off. They have a low toxicity level for humans making them one of the most widespread class of insecticides for plants in use today.
Why are neonicotinoids a concern?
The actual impact of neonicotinoids on pollinating insects is difficult to measure. However, recent studies have led researchers to believe that neonicotinoids not only affect targeted pest insects, but may also be harmful to non-target beneficial pollinating insects including bees and butterflies, as well as moths, wasps, flies, and beetles. A large concern is the high occurrence of neonicotinoids in home garden products.
Where can I find plants that have not been treated?
Determining if a plant had been treated with neonicotinoids is not always easy. There are no regulations requiring that plants treated with neonicotinoids be labeled. To guarantee you are purchasing plants that have not been treated with neonicotinoids, contact local plant nurseries—particularly those carrying native plants—and ask if their plants have been treated.
Your local or state gardening extension or gardening club should be able to provide a list of native plant nurseries and native plant sales. In fact, some smaller independent garden centers have completely eliminated plants treated with neonicotinoids.


- Avoid using garden products that include neonicotinoids. The Xerces Society has compiled a list of home garden products that include neonicotinoid chemicals.
- Use native plants in your garden, which reduces the need for chemical treatments.
- Implement organic garden practices to attract beneficial insects that help keep pests in check.
- Ask nursery or garden center staff if plants have been treated with neonicotinoids.
- Tell retailers that their customers want neonicotinoid-free plants and labels on plants that have been treated with them.
- Check out the Garden for Wildlife Gardening Tips page for additional information on organic practices, native plants and more.
![]() Already have a wildlife-friendly garden? Then certify it today!
Already have a wildlife-friendly garden? Then certify it today!